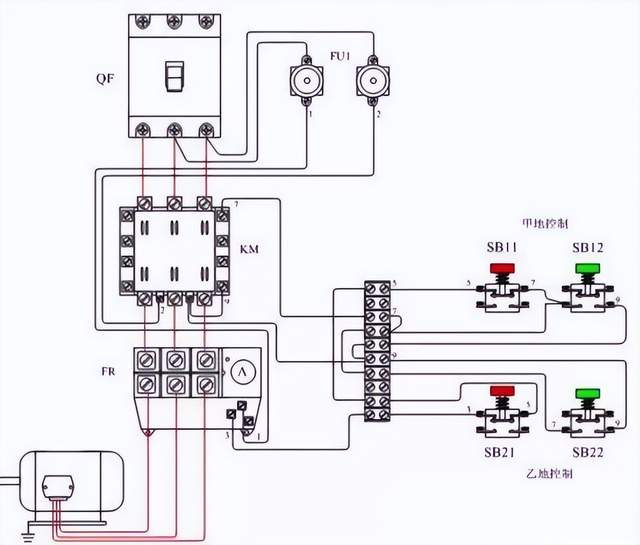
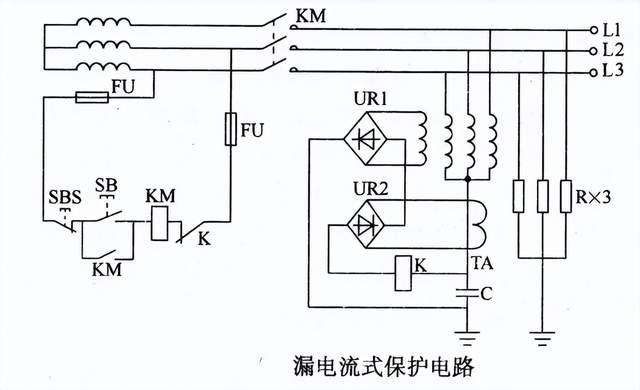
Every electrical equipment used in the power grid or in our daily life will have a rated power, when the power of the equipment is higher than the rated power, we call it overload.
Similarly, we call this protection over the rated power overload protection.
Another point to mention here is that when the equipment is overloaded, it is easy to cause a short circuit in the electrical equipment.
We call short-circuit protection for those that specifically prevent short-circuit faults inside the device.
What is overcurrent?
– –
Overcurrent and overload are both states, in which overcurrent is an operating state of electrical equipment when the motor or other electrical components are higher than the rated current.
Normally, the overcurrent is not higher than the short-circuit current and is within six times the rated current.
Overload protection
– –
The overload operating state belongs to the category of overcurrent operating state, because it is the state in which the operating current of the motor exceeds the rated current and is within 1.5 times.
If the electrical equipment is in a state of overload operation for a long time, the temperature rise of its windings will exceed the allowable value, resulting in aging or damage to the winding insulation.
Overload protection is often achieved through thermal relays, which can act instantaneously without being affected by the short-term overload surge current or short-circuit current of the motor.
However, it is also necessary to use a fuse or a low-voltage circuit breaker at the same time, because when the current exceeding 6 times the rated current passes through the thermal relay, it will be slow to occur, at least after five seconds.
This will cause the heating element of the thermal relay to be burned out when it starts.
Overcurrent protection
– –
As we mentioned earlier, overcurrent is a state, and when there is overcurrent, it is often smaller than the short-circuit current, and it is within six times.
Normally, in electrical circuits, the probability of short circuits occurring is much smaller than that of overcurrent, especially when the motor starts and reverses frequently.
It should be mentioned here that when there is an overcurrent in the line, if the current value can be returned to normal before reaching the maximum temperature rise, then the electrical components can still operate normally.
However, there is one point, the overcurrent here may cause the impulse current to damage the motor, and the instantaneous electromagnetic torque will damage the mechanical transmission parts, so it is necessary to cut off the power supply in time.
Overcurrent protection should use an overcurrent protection relay, which is installed in the protected line, when the current reaches a set value, the relay will act, its normally closed contact is connected in series in the branch where the contactor coil is located, so that the contactor coil is de-energized, and then disconnected through the main contact of the contactor in the main circuit, so that the motor power source is cut off in time.
Short-circuit protection
– –
Many novices do not know that in the power system, if the electrical equipment in the line or the insulation of its wiring is damaged, there may be wiring errors or load short circuits, etc., then the equipment will have short circuit failures when such situations occur.
When a short circuit fault occurs, the instantaneous current of the appliance is not only a little higher than the rated current, but dozens of times more.
Such consequences may be due to the appearance of strong electric power in the electrical circuit, which damages electrical equipment and generates an electric arc, which can lead to a fire with serious consequences.
Therefore, we need to take some measures to avoid the harm caused by short circuit faults, which is short-circuit protection. This requires us to quickly cut off the power supply after a fault, and the method often used here is to install a fuse or a low-voltage circuit breaker in the electrical line.